The tech giant meta, owner of Facebook, Whatsapp and Instagram, has made an important revelation about how its Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems determine what users see on its platforms. The main commitment of the company, as they themselves comment, is to increase the transparency and provide greater control to the user about its content.
Artificial Intelligence in Meta
Meta’s AI systems take care of classifying and displaying content on Facebook and Instagram. These systems consider factors such as user behavior, comments, and other elements to display the content that may be most relevant to each person. The AI is in charge of personalizing the experience of each user on the platform.
For the recommendations to be effective and relevant, it is essential to understand the content of the advertisements. For this, Meta uses AI techniques which include visual recognition, object detection, text extraction and audio recognition, among others. Using these techniques, Meta production models are capable of performing specific tasks, such as topic or genre classification, hashtag prediction, similarity matching, and clustering.
How do AI systems work?
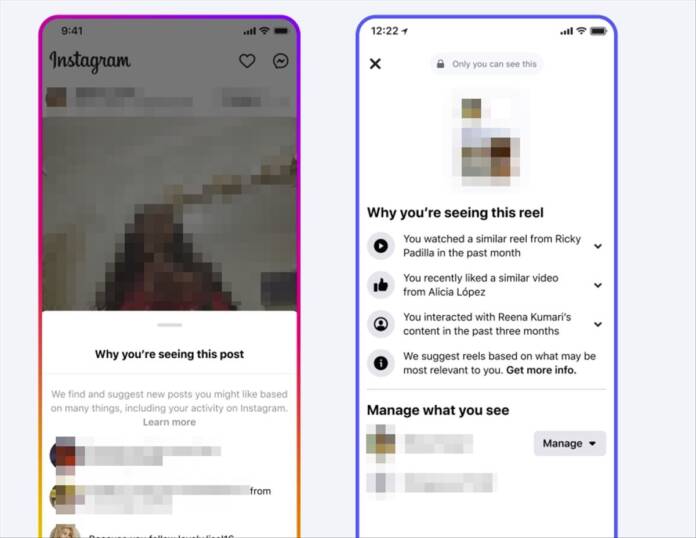
Meta is making the operation of its systems public by releasing 22 “system cards”. These cards explain how the content is classified, what predictions are made, and what controls are available to the user. The goal is to provide a better understanding of how AI ranks and recommends content.
Once the content has been understood and classified, it is necessary to identify what content is relevant to each user. For this, Meta has developed recovery and sorting systems that in fractions of a second they are able to reduce billions of pieces of content to a few hundred that are relevant to a user’s interests. These systems are based on large-scale attention models, graphing neural networks, and few-shot learning, among other techniques.
Signals and Predictions
The signs and predictions they are the inputs that the AI uses to classify and recommend content. Meta will publish details about these signals and predictions on its Transparency Center. This section also includes signals used to identify and reduce harmful or problematic content.
The cold start problems They are presented when new users or content enter the platform. To meet this challenge, Meta developed a few-shot learning system that can accurately match new content to potential audiences, even when there are few interactions.
To learn how different interests are related, embedding and graph learning techniques are used, as well as uncertainty modeling combined with reinforcement learning.
Harmful and problematic content
Meta uses specific signals to identify harmful content, which is removed as it is detected. It also employs signals to reduce the distribution of problematic or low-quality content in accordance with its Content Distribution Guidelines.
Custom Control
Users will now have more control over what they see in their feeds. Meta is expanding its feature «Why am I seeing this?“, which explains why certain content is displayed. Additionally, settings are being centralized to control the content viewed on Facebook and Instagram.
The system not only relies on content and user preferences to make recommendations, but also takes into account user behavior and feedback. AI systems respond to user interactions, refining the model of user preferences. Thus, systems can consider signals that show that a user is not interested in a certain type of content, such as watching a recommended video for only a few seconds before stopping it.
customization tools
New features are being tested and rolled out that allow users to further customize their feeds, such as indicating interest in recommended content, prioritizing certain accounts, and viewing content chronologically.
Tools for Researchers
Meta seeks to make it easier for researchers to understand their systems by releasing AI models, libraries, and data sets. A new suite of tools for researchers will be launched that will allow them to study data from public publications and business accounts on their platforms.
Finally, what this news leaves us is a glimpse into the future of social media. A future where users have more direct control over the content they see and where tech companies become more transparent about their internal processes. All of this points to a digital ecosystem where transparency and personalization could become the norm, not the exception.
Learn more at about.fb.com.